Curated foreign policy and national security news for professionals.
Good morning,
Let’s jump right into the Thursday morning brief.
Reporting Period: October 27-30, 2025
Bottom-Line Up Front:
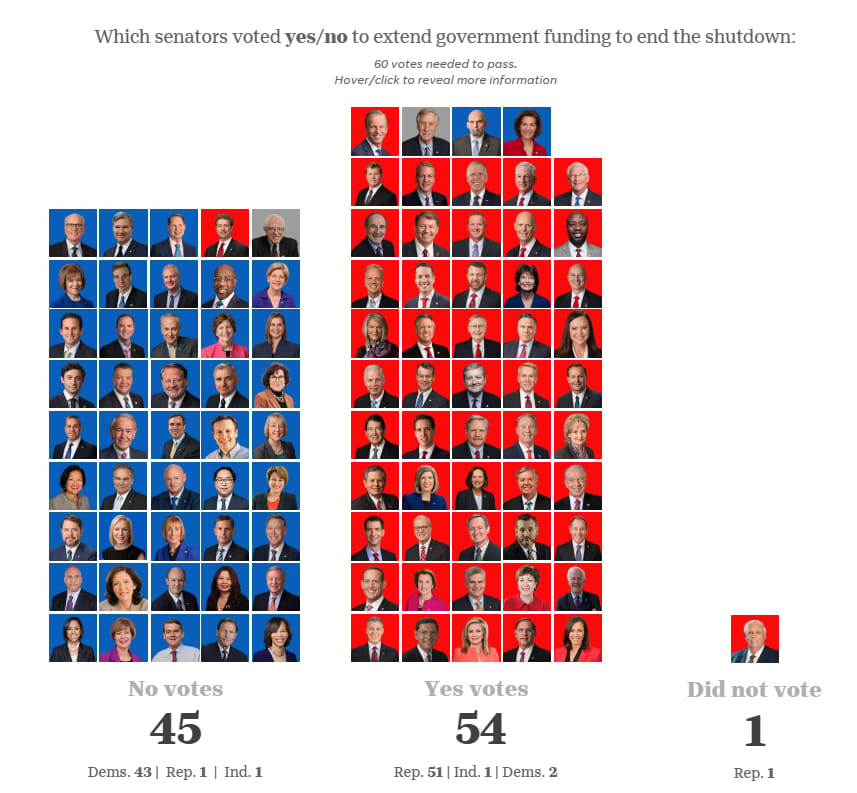
1. On October 28, the United States Senate failed to advance a Republican funding bill, perpetuating the ongoing government shutdown. The Trump administration stated that it will be able to pay active duty military personnel on Friday, October 31, despite funding running out. Full stoppages in pay are likely to begin in mid-November, increasing the risk to global force readiness, morale, and recruitment, as well as the defense industrial base.
2. On October 28, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu confirmed that he had ordered the Israeli military to conduct “powerful strikes” in the Gaza Strip. Netanyahu cited violations of the ceasefire by Hamas. Netanyahu states that Hamas did not honor terms of the ceasefire, and that hostages remain in Hamas custody. The move highlights the fragilities of the U.S.-brokered truce and regional stability.
3. President Trump and Prime Minister Takaichi held their first official visit in Tokyo, Japan, during Trump’s Asia tour. The pair signed a trade and investment deal, which focuses on Japanese investment into U.S. industries in exchange for lowered tariffs. The leaders also signed a landmark agreement on critical minerals and affirmed the need to deepen defense cooperation to advance the "free and open Indo-Pacific" policy agenda. The visit highlights a mutual desire to establish a "new golden era" for the U.S.-Japan relationship.
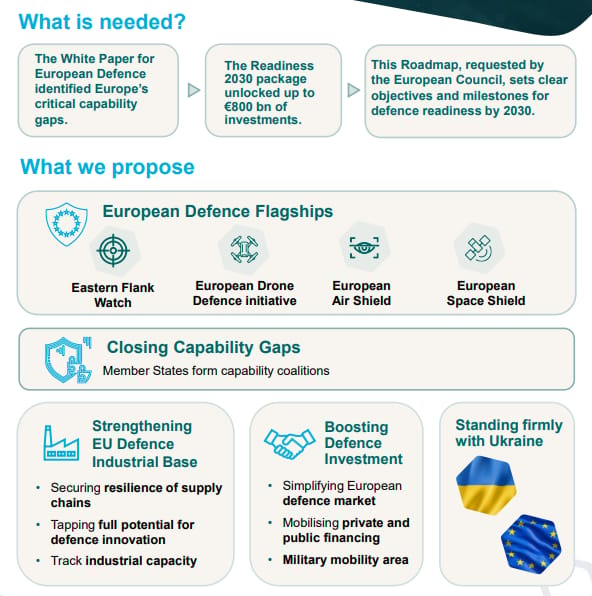
4. On October 29, the European Union published a document outlining goals and constraints to the EU’s “Defence Readiness Roadmap 2030” policy. The published roadmap illustrates the plan for Europe’s rapid defense build-up despite issues regarding funding, member support, existing capabilities, and allied coordination.
Government Shutdown Continues, Increases Risk Of Military Going Without Pay, Budgets
Summary
On October 28, the United States Senate failed to advance a Republican funding bill, perpetuating the ongoing government shutdown. The Trump administration stated that it will be able to pay active duty military personnel on Friday, October 31, despite funding running out. Full stoppages in pay are likely to begin in mid-November, increasing the risk to global force readiness, morale, and recruitment, as well as the defense industrial base.
Findings
Government Shutdown: On October 1, 2025, the U.S. government shut down due to Congress failing to pass an appropriations bill for FY2026 (NCSL, The White House). On October 28, Senate Democrats blocked the bill for the 13th time (CBS News). The bill requires 60 votes to pass, with 54 senators voting in favor and 45 voting against (CBS News). The government has been shut down for more than 29 days.
Risk to Warfighters: U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said that active duty troops will begin working without pay by November 15 (USA Today). The next military pay period is October 31, which Vice President Vance stated will be covered (USA Today, CBS News). On October 11, President Trump directed Secretary of War Hegseth to use $8 billion in Pentagon research, development, testing, and evaluation funds (The Hill).
Major pay discrepancies, with personnel being underpaid or not paid at all, pose risks to the financial stability of military families and unit morale (Federal News Network). The continued shutdown also scrutinizes the opinion of military service, likely hurting recruitment.
Why This Matters
The domestic effects of the government shutdown are one issue, but the risk to America’s military and national security apparatus is its own.
Troops going without pay, and service branches going without budgets, pose significant and varied risks to the military:
Military personnel dipping into savings to care for their families.
Military personnel losing faith in their institution, lowering morale and retention.
Lack of budgets leads to units canceling training, operations, maintenance, or timely deployments.
Lack of pay and budgets damages the military’s reputation as a reliable career, hurting recruitment and retention.
Reserve and National Guard forces remain idle, canceling training periods, exercises, procurement, etc.
Pause on federal contracts, or pulling from adjacent funds, weakens long-term strategic efforts.
In general, the shutdown demonstrates how Washington’s politicking and party dysfunctions create, or exacerbate, national security risks regardless of foreign threats.
Israel Orders New Strikes On Gaza, Ceasefire Broken
Summary
On October 28, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu confirmed that he had ordered the Israeli military to conduct “powerful strikes” in the Gaza Strip. Netanyahu cited violations of the ceasefire by Hamas. Netanyahu states that Hamas did not honor terms of the ceasefire, and that hostages remain in Hamas custody. The move highlights the fragilities of the U.S.-brokered truce and regional stability.
Findings
Background: On October 13, President Trump and Middle Eastern leaders signed “The Trump Declaration for Enduring Peace and Prosperity” (The Intel Brief). The declaration outlined steps and phases for restoring peace to Gaza, and identified ceasefire terms for the involved parties, including prisoner exchanges, troop withdrawals, and the governance of Gaza (The Intel Brief).
Original assessment by The Intel Brief indicated a likelihood of continued violence due to Israel’s desire to continue military operations in the West Bank, extrajudicial killings and factional violence in Gaza, and Netanyahu’s absence from the “Peace in the Middle East” Summit in Egypt (The Intel Brief).
Broken Ceasefire Allegations: Israeli troops stated they were shot at in Rafah before returning fire (CBS News). Israel states Hamas returned a coffin without the remains of a deceased hostage, to which Hamas said it will now delay the body’s return (BBC). Hamas calls the renewed strikes and military actions a violation of the terms, and that Israel has been obstructing Hamas’ humanitarian efforts (BBC).
Why This Matters
President Trump was questioned about the development and stated that “nothing’s going to jeopardize” the ceasefire and that the Israeli soldiers who were fired at “have a right” to retributive strikes. No details were provided, but given Trump’s remarks (stating a single soldier was killed by sniper fire) and Netanyahu’s recent post on X, we can infer the identity of the IDF victim:
Trump also remarked that Hamas “will be terminated” if the war continues, previously suggesting the U.S. may assist Israel with future operations.
As of now, there are 13 bodies that still need to be handed over to Israel. Hamas stated it will now intentionally delay the handover, suggesting a total collapse of the ceasefire if no diplomatic intervention is made.
Trump Meets With New Japanese Prime Minister, Signs Trade Deal
Summary
President Trump and Prime Minister Takaichi held their first official visit in Tokyo, Japan, during Trump’s Asia tour. The pair signed a trade and investment deal, which focuses on Japanese investment into U.S. industries in exchange for lowered tariffs. The leaders also signed a landmark agreement on critical minerals and affirmed the need to deepen defense cooperation to advance the "free and open Indo-Pacific" policy agenda. The visit highlights a mutual desire to establish a "new golden era" for the U.S.-Japan relationship.
Findings
Trump-Takaichi Meeting: On October 28, President Trump and Prime Minister Takaichi held a U.S.-Japan Summit in Tokyo, marking the pair’s first official meeting. Secretary of State Rubio and Secretary of War Hegseth also met with their Japanese counterparts.
Investment for Lower Tariffs: The core of the economic agreement involves Japan's pledge to inject $550 billion in investment into the U.S. economy (CBS News, Japan Times). In return, the U.S. implemented a 15% tariff on imported Japanese goods, a notable reduction from the 25% tariff previously threatened by the Trump administration (CBS News, Japan Times).
Targeted U.S. Investments: The Japanese investment is earmarked for key U.S. industries to strengthen the industrial base and supply chains (The White House). Commitments announced include:
Energy Infrastructure: Up to $332 billion for critical energy projects, including the construction of advanced nuclear reactors (AP1000 and Small Modular Reactors—SMRs) in partnership with companies like Westinghouse, GE Vernova, and Hitachi (The White House).
Technology and AI: Significant funding is allocated for AI infrastructure, advanced electronic components, data center power systems (Mitsubishi Electric), and optical fiber cables (Fujikura) (The White House).
Critical Minerals: Investment into new facilities for high-pressure diamond grit manufacturing and a lithium-iron-phosphate production facility to boost domestic supply (The White House).
Critical Minerals and Rare Earths Pact: The leaders signed a separate, strategic agreement to secure the supply chains for critical minerals and rare earths (TRT World). This includes plans for both countries to coordinate investment and policy efforts to establish diversified, non-Chinese sources for these materials, which are essential for advanced technologies and defense (The Guardian).
Defense and Security: Prime Minister Takaichi committed to fundamentally reinforcing Japan's defense capabilities and pledged to accelerate the increase of defense spending to 2% of GDP ahead of schedule (Japan Times). The U.S. welcomed these measures, along with Japan's purchases of U.S. defense equipment.
Why This Matters
The Trump-Takaichi visit and the finalized agreements mark a significant, transactional shift in the nature of the U.S.-Japan alliance, primarily motivated by economic security and the geopolitical competition with China.
The $550 billion Japanese investment, tied to favorable tariff rates, not only boosts the U.S. industrial base in critical strategic sectors like energy, defense, and technology, but also improves the base for which the U.S. engages in other bilateral trade.
The rare earths agreement directly addresses a major strategic vulnerability for both nations by coordinating efforts to reduce reliance on China for materials vital to modern defense systems and digital technologies. Combined with Japan's accelerated commitment to the 2% defense spending target, the summit signals a renewed, unified, and capable leading cohort in the region, and one that is particularly geared for strengthening deterrence and promoting the "free and open Indo-Pacific" policy agenda.
EU Publishes List Of Constraints To Defence Readiness Roadmap 2030
Summary
On October 29, the European Union published a document outlining goals and constraints to the EU’s “Defence Readiness Roadmap 2030” policy. The published roadmap illustrates the plan for Europe’s rapid defense build-up despite issues regarding funding, member support, existing capabilities, and allied coordination.
Findings
Sustained Funding and Political Will: While defense budgets are rising, the roadmap's success hinges on whether governments can maintain a unified commitment and spend more efficiently (Centre for European Reform). Funding increases typically take time to translate into concrete capabilities, and there's a risk of new investments being wasted without better coordination and decisionmaking (Centre for European Reform).
Persistent Capability Gaps: European forces still have large, critical shortfalls in key modern military domains, particularly in air defense, long-range strike capabilities, intelligence gathering, and command and control systems, as well as personnel shortages (Centre for European Reform).
Fragmentation and Duplication: The core challenge is the coexistence of national defense plans, NATO's strategy and commitments, and new EU initiatives (Centre for European Reform). This results in the continued fragmentation of the European defense industrial base which leads to duplication of efforts, as member states often prioritize national issues before supranational ones.
Replacing Versus Building: Much of the recent equipment procurement serves only to replace systems donated to Ukraine, meaning that overall, the collective European stock of advanced military equipment is not rapidly expanding, but being depleted (Centre for European Reform).
The "Sovereignty Trilemma": Achieving the full ambition of strategic autonomy requires EU member states to solve a difficult political trilemma: they must either accept substantial impacts on other policy areas, implement significant tax hikes, or agree to cede the exercise of sovereignty over aspects of their national defense (a step most member states remain reluctant to take) (Centre for European Reform).
You can read the whole “Defence Readiness Roadmap 2030” here.
Why This Matters
The constraints identified in the roadmap highlight the fragility of a European Union-led defense reform, especially as those efforts compete directly with NATO ones.
The greatest risk to the initiative is funding and transnational support. If these foundational hurdles are not overcome, the EU will fail to achieve genuine strategic autonomy, limiting its influence in the region and within its own bloc, and remaining unprepared for a conflict with Russia.
End Brief
That concludes this brief. Thank you for reading!
See you Sunday,
— Nick
This publication is an Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) product and does not contain Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) or Classified Information.